Gary Ruvkun is a groundbreaking figure in genetic research, celebrated for his pivotal discovery of microRNA alongside Victor Ambros that earned them the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. This monumental achievement underscores the significance of gene regulation, particularly within the realm of Harvard genetics, where Ruvkun serves as a distinguished professor. Initially met with skepticism, their research on microRNAs, published in 1993, demonstrated a foundational role in the regulation of genes across species, igniting interest that has only intensified over the decades. Much of this progress has been made possible through federal funding in science, which Ruvkun highlights as crucial for supporting innovative research initiatives. As microRNA therapies move into clinical trials for various diseases, Ruvkun’s contributions continue to shape the future landscape of biomedicine.
The narrative of Gary Ruvkun’s scientific journey reveals a profound impact on the landscape of genetic research, particularly regarding the pivotal role of small RNA molecules known as microRNAs. His early work, paired with Ambros, laid the groundwork for a new understanding of how genes are regulated, an area that has become increasingly important in modern biology. Despite initial doubts from the evolutionary biology community, Ruvkun’s findings have sparked a surge of interest across multiple fields, illustrating the interconnectedness of life sciences. The support from federal initiatives has been essential in fostering this groundbreaking research, highlighting the importance of public investment in science for driving innovation. As we explore the implications of gene regulation on health and disease, Ruvkun’s story stands as a testament to the power of persistence and discovery in the scientific realm.
The Journey from MicroRNA Discovery to the Nobel Prize
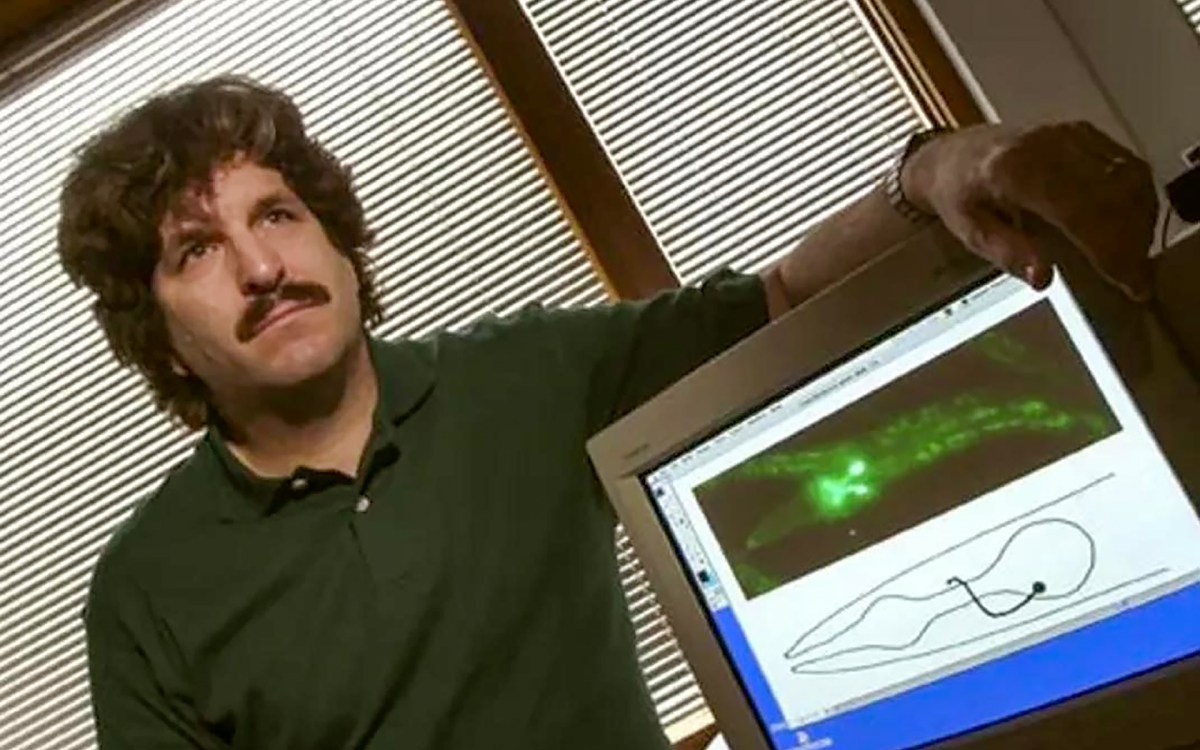
Gary Ruvkun and his collaborator, Victor Ambros, made a groundbreaking discovery in the early 1990s that would eventually earn them the 2024 Nobel Prize. Initially, their work on microRNA was not widely recognized or appreciated within the broader scientific community. Their publication in 1993 in the journal Cell did shed light on a new dimension of gene regulation through microRNAs in the C. elegans roundworm, but the evolutionary biology sector was skeptical of its relevance to other species, including humans. Over the years, however, awareness of the significance of microRNA continued to grow among a niche group of RNA researchers, and the revolutionary implications of their findings became clearer.
As research on microRNAs progressed, distinct connections were made between these tiny RNA molecules and their regulatory roles in various organisms. Ruvkun noted a significant increase in interest as scientific meetings that once only attracted a small audience began to expand rapidly. This surge in engagement illustrated a fundamental shift in the understanding of gene regulation, with researchers from multiple disciplines recognizing microRNAs’ critical function across different biological contexts. Ruvkun’s realization that they were pioneering a revolutionary concept laid the groundwork for decades of further advancements in genetics.
Ruvkun’s journey illustrates how sustained dedication to fundamental research, backed by federal funding, can result in accolades such as the Nobel Prize. Their initial discovery was merely the tip of the iceberg, revealing a vast field of study that now influences numerous medical therapies and scientific approaches.
The advances in understanding microRNA and gene regulation have catalyzed significant breakthroughs in the medical field, solidifying the importance of basic science research. Consequently, Ruvkun’s contributions have not only shaped the field of genetics but have also paved the way for innovative approaches to treating complex diseases.
The Role of Federal Funding in Scientific Advancements
Gary Ruvkun’s research journey has been significantly supported by federal funding, primarily from the National Institutes of Health (NIH). Over 40 years, he noted that approximately 75% of his lab’s work was financed through federal grants, emphasizing the critical nature of such support in scientific endeavors. Ruvkun’s experience showcases how secure funding allows scientists to explore and develop novel ideas without the constraints of commercial pressures. With an annual budget averaging around $150,000, his lab has been able to maintain a focused team, underscoring the necessity of robust financial resources in producing groundbreaking research.
Unfortunately, amidst discussions about budget cuts to scientific research, Ruvkun expressed concerns about the potential ramifications of reduced federal funding. He articulated the fear that diminishing support could deter young scientists from pursuing careers in research, especially as many consider relocating to Europe for stable roles in science. The scenarios he outlines depict a troubling future for American science, which has historically thrived on government investment in research and innovation. Ruvkun insists that federal funding is not only justified but essential for maintaining the United States’ status as a leader in scientific inquiry and discovery.
Without sustained investment, the pipeline of new discoveries in genetics, such as those involving microRNA, could stagnate, ultimately impacting clinical applications and public health. Ruvkun’s perspective serves as a poignant reminder of the interconnectedness of research funding and scientific progress, reinforcing the role of governmental support in paving the way for revolutionary breakthroughs.
The discussion around federal funding also points to the broader implications for industries relying heavily on scientific research and its outcomes. Major pharmaceutical companies have emerged from this foundational work, showcasing the economic benefits stemming from strong government investment in science. Ruvkun advocates for a reassessment of funding policies to ensure that research remains a priority, especially considering the potential compounded benefits for society at large.
Implications of MicroRNA Discoveries in Medicine
The discovery of microRNAs by Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros brought forth a transformative understanding of gene regulation that reverberates through modern medicine. MicroRNAs play crucial roles in a wide array of biological processes, including how cells develop and function. Today, it is estimated that human beings possess approximately 1,000 microRNAs that significantly influence the expression and activities of most protein-coding genes. These tiny molecules have gained immense attention for their potential therapeutic applications, particularly in tackling some of the most pressing health challenges.
Therapies designed around the modulation of microRNAs are currently being tested in clinical trials for various diseases, including cancer, heart disease, Crohn’s Disease, and Alzheimer’s. The capacity of microRNAs to control gene expression provides a powerful mechanism for developing novel treatments that could offer targeted interventions with fewer side effects. Ruvkun emphasizes the significance of these advancements, pointing out that they demonstrate how basic research can yield practical applications that can fundamentally change patient care and treatment approaches.
As the role of microRNAs continues to expand in the therapeutic landscape, it exemplifies the broader implications of fundamental discoveries in genetics. The ongoing research driven by Ruvkun and his contemporaries highlights the intricate connection between basic science and advanced clinical solutions, encouraging further investigation into the vast potential of gene regulation through microRNAs.
In summation, the landscape of modern medicine is being reshaped by the insights gained from microRNA research, demonstrating how foundational discoveries can influence the trajectory of scientific inquiry and medical innovation. Ruvkun’s work stands as a testament to the power of curiosity-driven research in yielding significant societal health benefits, making it an essential area of focus for future developments in genetics and therapy.
Educational Impact of Ruvkun’s Research
Gary Ruvkun’s work in genetics has also had profound educational implications, particularly for future generations of scientists. As a professor at Harvard Medical School, he has been instrumental in mentoring young researchers in the field of genetics, instilling in them the importance of innovation and curiosity. His groundbreaking discovery with microRNAs has not only transformed scientific understanding but has also served as a critical case study in the biochemistry curriculum, illustrating the path from basic research to significant breakthroughs in medicine.
Ruvkun’s experience highlights the necessity of integrating research findings into educational settings, allowing students to witness the real-world application of theoretical knowledge. His mentorship has inspired many upcoming scientists to pursue careers in genetics and molecular biology while emphasizing the values of rigorous inquiry and persistence in scientific research. By discussing the challenges faced early in their careers, Ruvkun encourages students to embrace curiosity and the persistence necessary to lead change in science.
The evolving landscape of genetic research necessitates an educational framework that prepares students to tackle complex questions in the field. Ruvkun’s efforts in education underscore the importance of fostering a new generation of thinkers who will carry forward the legacy of innovation and discovery, anchored in the foundational work established over the last few decades.
Ultimately, the integration of Ruvkun’s pioneering research on microRNAs in educational programs serves as a powerful tool for engaging students and illustrating the relevance of genetic research in societal health. As emerging scholars continue to build on this work, the educational impact will ripple throughout the scientific community, inspiring sustained interest and inquiry into the vast realm of genetics.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role did Gary Ruvkun play in the discovery of microRNA?
Gary Ruvkun, alongside Victor Ambros, discovered microRNA in 1992, which fundamentally shaped our understanding of gene regulation. Their research, published in 1993, identified how tiny RNAs regulate genes, a breakthrough that ultimately led to them receiving the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine.
How did federal funding impact Gary Ruvkun’s research at Harvard?
Federal funding has been vital for Gary Ruvkun’s research on microRNA, with approximately 75% of his lab’s budget supported by NIH grants over the last 40 years. This funding, averaging $150,000 a year, has allowed him to maintain a focused research team, contributing significantly to advancements in gene regulation.
What are the implications of Gary Ruvkun’s microRNA discovery for human health?
Gary Ruvkun’s discovery of microRNA is crucial for human health, as these small molecules play a key role in gene regulation and protein production. Current research based on microRNA is paving the way for innovative therapies for diseases such as cancer, Alzheimer’s, and heart disease, highlighting their significance in medical science.
How did the scientific community react to Gary Ruvkun’s findings on microRNA in the early 1990s?
Initially, the scientific community was skeptical of Gary Ruvkun’s findings on microRNA. After their publication in 1993, interest was limited to a niche group of RNA researchers and the ‘worm community.’ However, as the field grew, it became clear that microRNAs have critical functions across various organisms, including humans.
What is the significance of the Nobel Prize 2024 awarded to Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros?
The Nobel Prize 2024 awarded to Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros underscores the monumental impact of their discovery of microRNA on molecular biology and medicine. This recognition highlights the importance of their research in advancing our understanding of gene regulation and its implications for treating diseases.
What can we learn from Gary Ruvkun’s long journey in RNA research?
Gary Ruvkun’s journey in RNA research demonstrates that groundbreaking discoveries can take years to gain recognition and funding. His persistence, supported largely by federal funding, illustrates the need for continued investment in basic science to fuel innovation and breakthroughs in genetics and medicine.
How has Gary Ruvkun contributed to advancements in genetics through his research?
Gary Ruvkun has significantly advanced the field of genetics through his pioneering research on microRNA. His contributions have not only enhanced our understanding of gene regulation but have also led to the development of RNA-based therapies, showcasing the practical applications of his scientific work.
What concerns does Gary Ruvkun have regarding federal funding in science?
Gary Ruvkun expresses concerns that cuts to federal funding could deter young scientists from pursuing careers in research. He emphasizes the importance of sustained investment in science to nurture talent and maintain the innovative edge that has historically made the U.S. a leader in scientific discovery.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Discovery of microRNA | Gary Ruvkun and Victor Ambros discovered microRNA in 1992, leading to the 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. |
| Initial Reception | Their findings were initially met with skepticism and minimal interest in the broader scientific community. |
| Impact of Research | MicroRNAs are now known to regulate gene expression significantly, with over 1,000 identified in the human genome. |
| Therapeutic Applications | Research into microRNAs has led to potential treatments for diseases like cancer, heart disease, and Alzheimer’s. |
| Funding and Support | Approximately 75% of Ruvkun’s research has been funded by federal grants. |
| Economic Influence | Ruvkun notes that federal funding has been instrumental in the technological growth of the U.S., driving innovation in various sectors. |
| Concerns for Future | Ruvkun worries about the future of scientific research and talent retention in the U.S. due to potential cuts in funding. |
Summary
Gary Ruvkun’s groundbreaking work in the discovery of microRNA has had a profound and lasting impact on the field of genetics. From a modest beginning in the early 90s, his research journey reflects the transformative power of federally funded science. As we look forward, it is essential to recognize the critical role that continued investment in scientific research plays not just for individual careers, but for the overall advancement of human health and technology.